|
|
|

The characterization of the physical properties of biomaterials
such as biological soft and connective tissues
inherently requires the testing of such materials within a
simulated body fluid environment.
Because both of the detachable drums are cantilevered and
suspended from the SER3 base chassis,
the SER3 models
that are configured for use
on controlled stress/strain rotational rheometers such as the SER3-P,
SER3-G, SER3-T, and SER3-M are capable of fluid immersion testing.
The drums of said SER3 models
can be raised from and lowered into a controlled temperature
fluid environment contained within a jacketed beaker or other such
fluid containment vessel for the purposes of characterizing
the physical properties of natural or synthetic biomaterials.
In this manner, sample specimens can be easily loaded and unloaded
from the windup drums while the SER3 is completely raised from the
fluid surface.
The image below depicts a SER Universal Testing Platform hosted on an
Anton Paar
MCR host rotational rheometer suspended above a controlled temperature
fluid environment contained within a glass jacketed beaker.

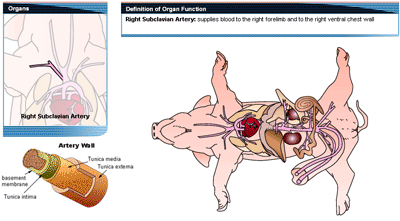
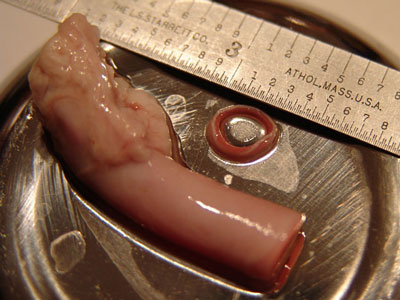
The following videos depict the tensile testing of a ring-shaped cross-sectional
blood vessel specimen dissected from a porcine right sublcavian artery as
illustrated in the above diagram and photo. The ring specimens were simply looped
around the securing clamps before clamp insertion into the windup drums
thereby defining a ring tensile test which is commonly used for
evaluating hoop stresses in pipes and
other such pressure conduits.
Note as well that all of the following videos
depict rough textured
SER3-DR drums
that were used in order to assist
in sample gripping during the stretching process within the fluid
environment.
Note that for all of the SER videoclips depicted below, the sample deformation remains
in a fixed plane and is ALWAYS
clearly and easily accessible for deformation visualization.
Also note how in all cases only
the drums of the SER need to be immersed within the fluid environment.
|
|

